
Sue Konzelmann
During the past decade – in the aftermath of the most serious financial and economic crises since the Great Depression – the question of why policy doesn’t always change when it looks like it ought to has been an open one.
This is especially true of Britain, where the combination of the lack of a fixed, written constitution and the nature of its political and institutional system, in theory at least, make it more prone to change than much of the rest of Europe.
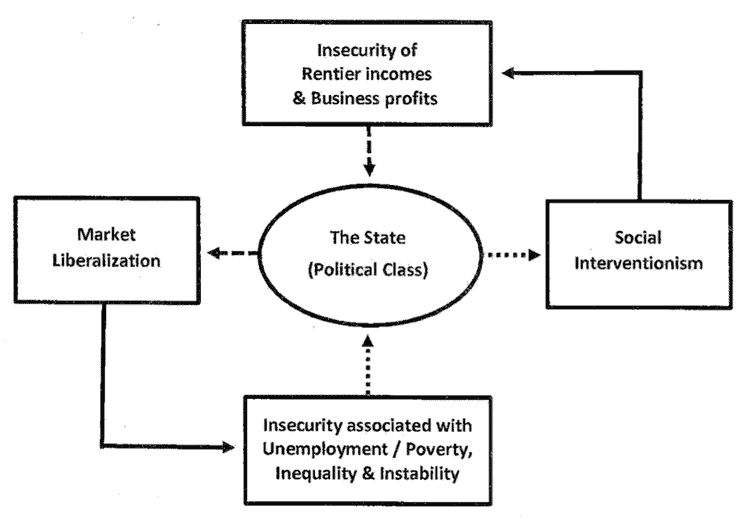
Examination of the major shifts in policy that have taken place since the dawn of industrial capitalism reveals an “insecurity cycle” at work. This policy cycle results from opposing interest groups – working classes on the one side and capitalists on the other – applying pressure on policy-makers to shift the focus of policy towards support of their own viewpoint and interests.
The insecurity cycle

Simon Deakin
Following periods of market liberalization, in response to the resulting insecurity associated with rising unemployment, poverty and inequality, those affected can be expected to put pressure on policy-makers for social intervention and protection. However, a counter-response by capital and those in upper segments of the distribution of income and wealth – pressuring policy-makers to scale back social protections and liberalize markets – is once again likely to follow. The perceived “zero sum” nature of this ongoing contest usually means that a gain for one side is seen as a loss by the other – inevitably resulting in push back and the continuation of the cycle.

Marc Fovargue-Davies
Historically, the significant asymmetry of power between the forces of free market capitalism and the social welfare state has meant that movement towards social interventionism has typically been long and drawn out, whilst shifts towards market liberalization have been relatively abrupt.
Winds of change
Research on the dynamics of major policy shifts – from the industrial revolution to the present – suggests that four main factors produce the conditions for a change. These include:
- Crisis – usually of considerable duration; but such a “chronic” crisis may be exacerbated by shorter, “acute” crises.
- Democratic pressure, often at its greatest during elections, can also be highly influential in between; over the years it has resulted in the emergence of trade unions, pressure for expansion of the franchise and, more recently, socially based movements – such as Momentum – on the social welfare side of the insecurity cycle. But not all democratic pressure is on this side of the cycle, with the 1978-79 “winter of discontent” producing a tide that swept Margaret Thatcher into office, illustrating the two remaining factors:
- New – or different – policy ideas;
- Credible political backing. Both of these were present in 1979, adding to both the chronic crisis of the 1970s, generally, and the acute crisis of the winter of discontent.

Frank Wilkinson
Combined with the resulting democratic pressure, change was almost as inevitable in 1979 as it had been less than four decades earlier, with the combination of the chronic crisis of the interwar years, the acute crisis of World War Two, the new ideas of John Maynard Keynes and the Labour Party, and a highly “electable socialist” in the form of Clement Attlee in 1945. The policy changes implemented after the elections of Attlee and Thatcher represent the two complete turns of the insecurity cycle so far, with the move to the left taking over 150 years, and that to the right a scant 35. There have, however, also been many smaller shifts, that could be accommodated within the existing policy paradigm.
Axis of anger
The insecurity cycle is also a useful way to help make sense of events both in Europe and on the other side of the Atlantic. This is a policy cycle that is not primarily driven by numbers and data, so much as by feelings of unfairness, hopelessness, and in some cases, anger and fear. As the Brexit campaign revealed, such feelings are difficult to dissipate by politicians citing indicators such as GDP or “happiness” coefficients in defense of the status quo, rather than implementing substantive changes in policy. From this perspective, the sharp polarization between support for the UK’s continued membership of the European Union, and those who feel it is damaging, as well as that between President Trump’s supporters in the US, and those who feel that they’ve lost out as a result of globalization, begin to make considerably more sense.
Is the insecurity cycle an inevitable part of policy-making? Perhaps – and if both sides continue to see it as a zero sum game, almost certainly. However, what if the relationship between labor, finance and the social welfare state could be fundamentally changed? Continued technological change, as well as expanding populations – both in a context of finite resources – would suggest an uncomfortable intensification of the insecurity cycle if this is not at least attempted.
The links between social movements like Momentum in the UK, and Our Revolution, which has grown out of Bernie Sanders’ presidential campaign in the US, offer the intriguing possibility that politicians like Jeremy Corbyn and Sanders – who are articulating an alternative vision of society and politics – may produce an axis as influential as that of Reagan and Thatcher during the 1980s. This, of course, would also mark a third complete movement in the insecurity cycle.
Based upon the authors’ book, Labour, Finance and Inequality: The Insecurity Cycle in British Public Policy, published today
Sue Konzelmann is a Reader in Management at Birkbeck, University of London. Simon Deakin is Professor of Law and Director of the Centre for Business Research (CBR) at the University of Cambridge. Marc Fovargue-Davies is a research associate with the London Centre for Corporate Governance & Ethics, contributing to multi-disciplinary projects. Frank Wilkinson is a former Research Officer in the University of Cambridge's Department of Applied Economics and currently Chairman of the Cambridge Political Economy Society.